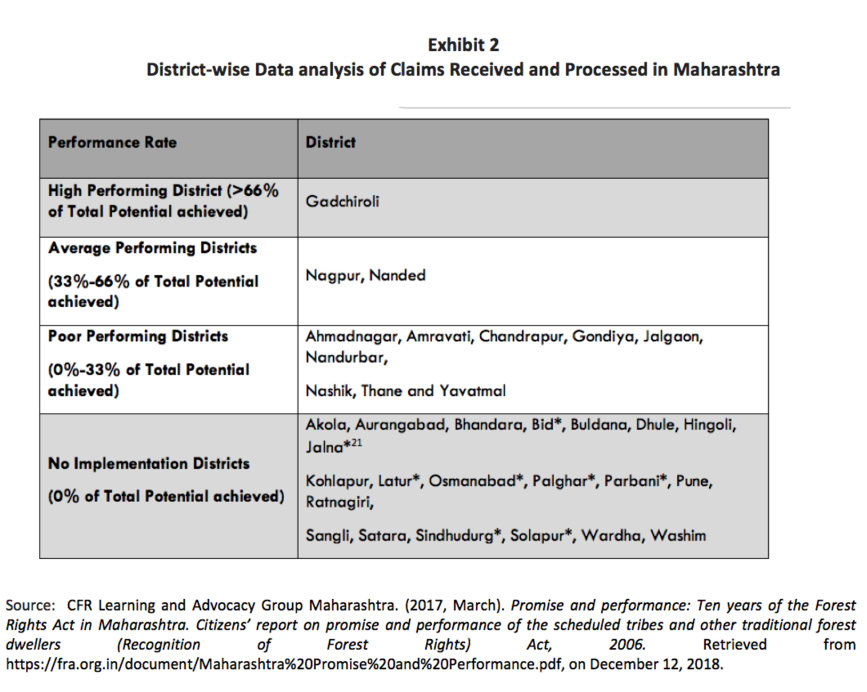
In spite of the law recognizing traditional forest dwellers’ rights to own land, 63% of districts in the state of Maharashtra have zero compliance. However, Gadchiroli district is the only exception.
Avijit Chatterjee , Mrinalini Paul, and Nikhila Chigurupati
The Forest Rights Act, 2006 recognizes forest dwellers’ rights to own and govern forest land in their possession. The thrust of the Act is to ensure local and self-governance of the forest rights by the community. With the forest being an invaluable resource, procuring land titles has been met with reluctance by government officials thereby making the implementation of the law slow or uncertain. Despite hurdles such as claim process delays, Gadchiroli district is a shining example with 66% of the title claims already processed.
COMMUNITY FOREST RIGHTS UNDER THE FOREST RIGHTS ACT, 2006
The Forest Rights Act, 2006 (The Act/FRA) was legislated by the Parliament of India to recognize the rights of traditional forest dwellers and Scheduled Tribes to forest land and resources. These rights, among others, included ownership and protection of land already in possession of the forest dwellers prior to December 13, 2005. The aim of the Act was to promote self-governance of forests and forest resources by local and forest dwelling communities. During our field study, we found many success stories in areas where there was evidence of effective implementation of the Act and direct community benefits. However, it was clear that these communities were still riding the learning curve in terms of exercising these rights in conducting business and earning their livelihood. Overall, the implementation of the Act had been poor due to various issues such as the limited admissibility of documents as evidence and claim process delays. However, we did find one district in Maharashtra to be a shining example, with 66% of community forest right claims having been processed. The take-away in the successful implementation of FRA in Gadchiroli district was the joint effort between the community and government officials. This was a model that could be replicated elsewhere. However, the reluctance of the Forest Department and government officials to follow this model and process claims in other states made the effective implementation of the FRA slow or uncertain across the country.
THE FOREST RIGHTS ACT, 2006
The Scheduled Tribes and Other Traditional Forest Dwellers (Recognition of Forest Rights) Act, 2006, was a historic piece of legislation that restored the rights of traditional forest dwellers to access, manage and govern forest lands and resources within village boundaries. These lands had been controlled by the forest department since the colonial era. Since 2006, under the law, traditional forest dwellers and STs could claim either individual or community forest rights (CFRs), thus taking ownership of the process of protecting and conserving forests in their areas. They could also gather and sell minor forest produce, such as tendu leaves (used to make traditional Indian cigarettes called bidis) or bamboo, which it had been illegal to do before the law was enacted. These rights over forest resources, therefore, allowed for positive livelihood outcomes and, in effect, also provided for the evolution of a livelihood-sensitive but ecologically sustainable system of local self-governance among forest dwelling communities.
Colonial era laws that had persisted through the post-independence period in India had denied forest dwellers rights to state forests until the enforcement of the Act. Under the British colonial regime, large pieces of these forested areas were brought under the legally classified category of “forest land” to serve as a direct source of timber or for the development of timber plantations. The customary rights of people living on or off the lands, now called forests, were first overridden by the British and subsequently remained inadequately recognized in the 60 years after Indian independence. Thus, traditional forest dwellers were treated as encroachers and evicted from forest lands, resulting in mass protests that eventually led to the passage of the Forest Rights Bill, 2005. Demands for regularization of rights based on land use and the use of village elder testimonies as proof of occupation raised the tenurial security issue. This presented a larger philosophical argument in favor of policy changes to the pre-independence classification of forest land, which had criminalized tribal and other forest dependent communities. The movement eventually gained momentum, leading to the passage of the FRA in Parliament in December 2006.